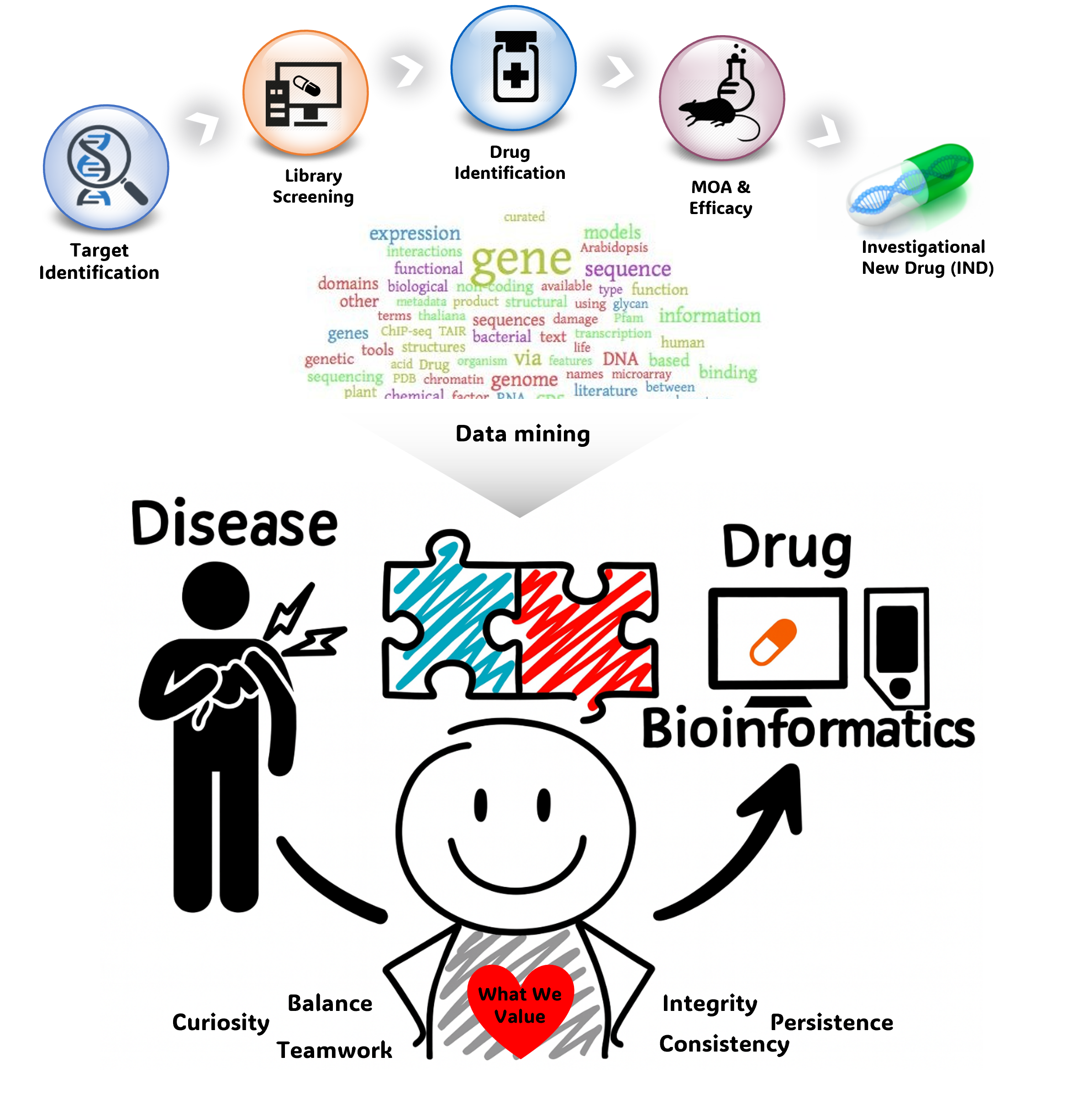
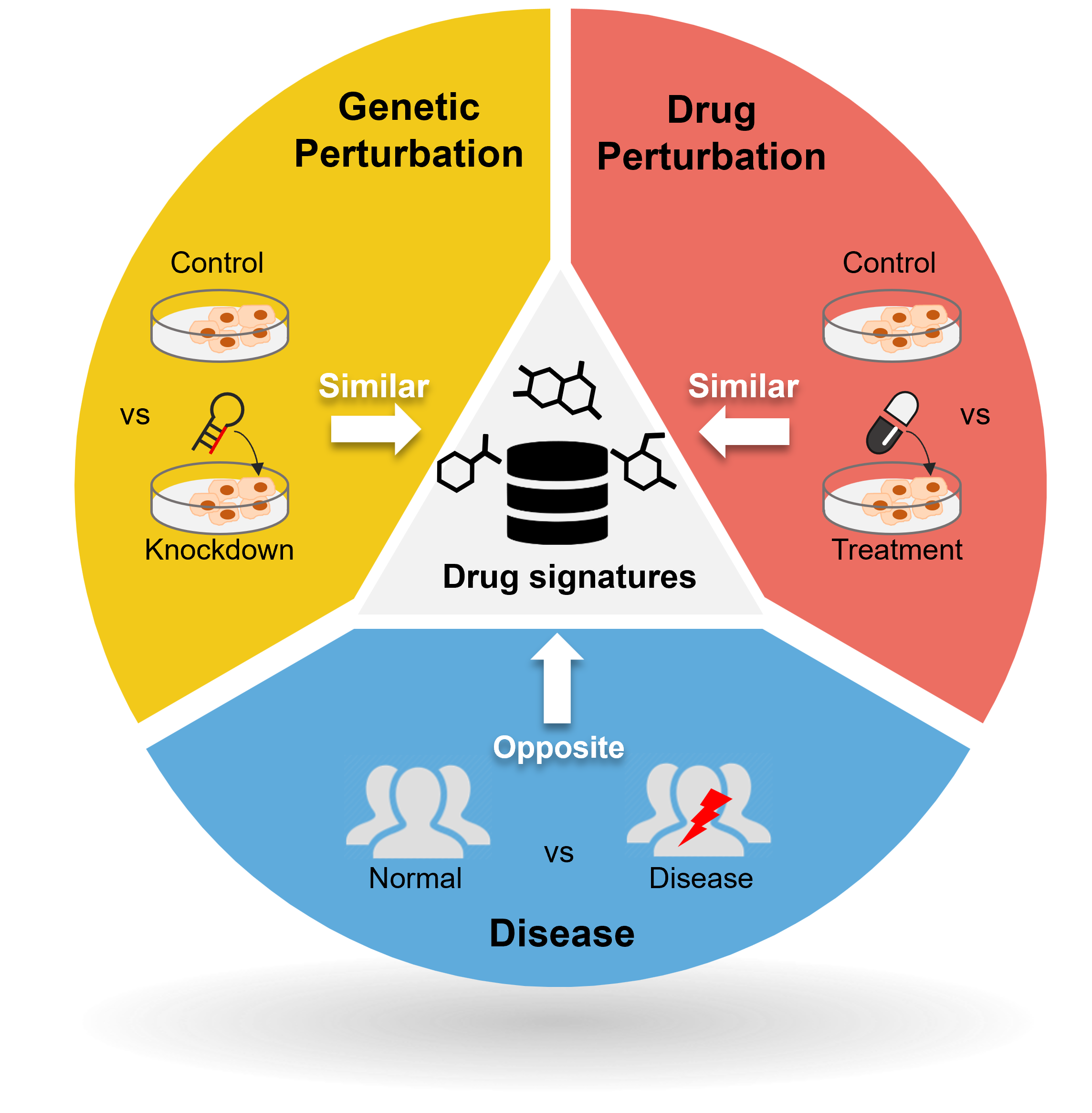
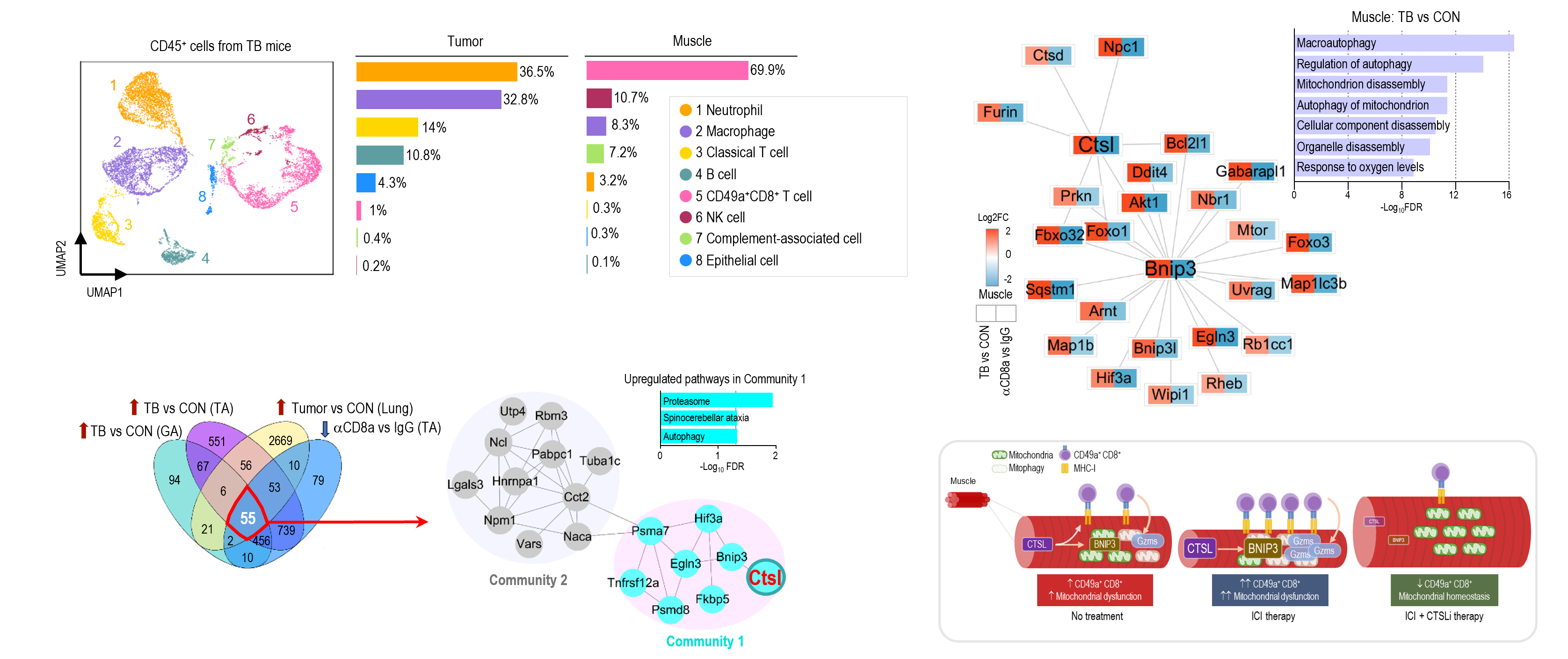
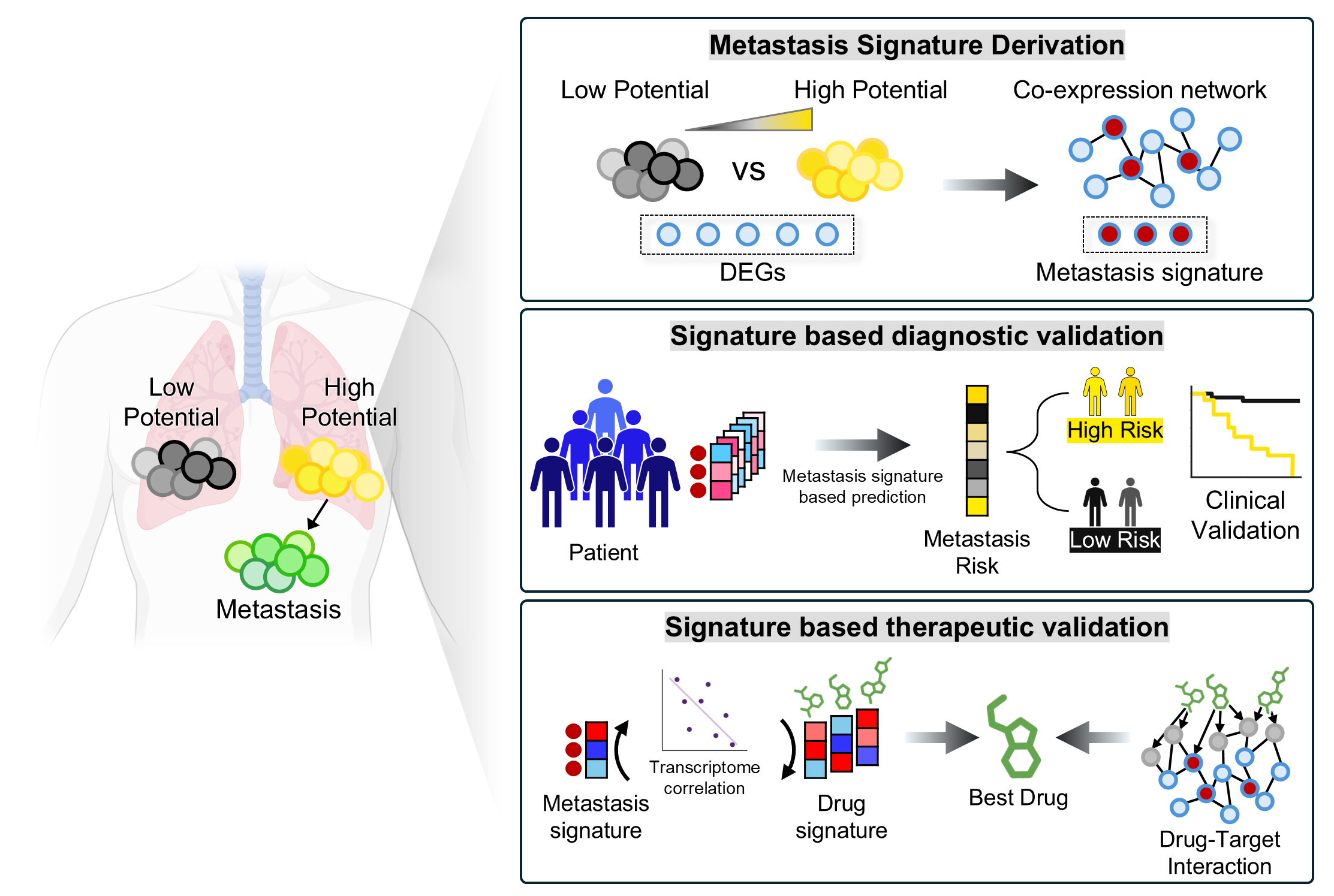
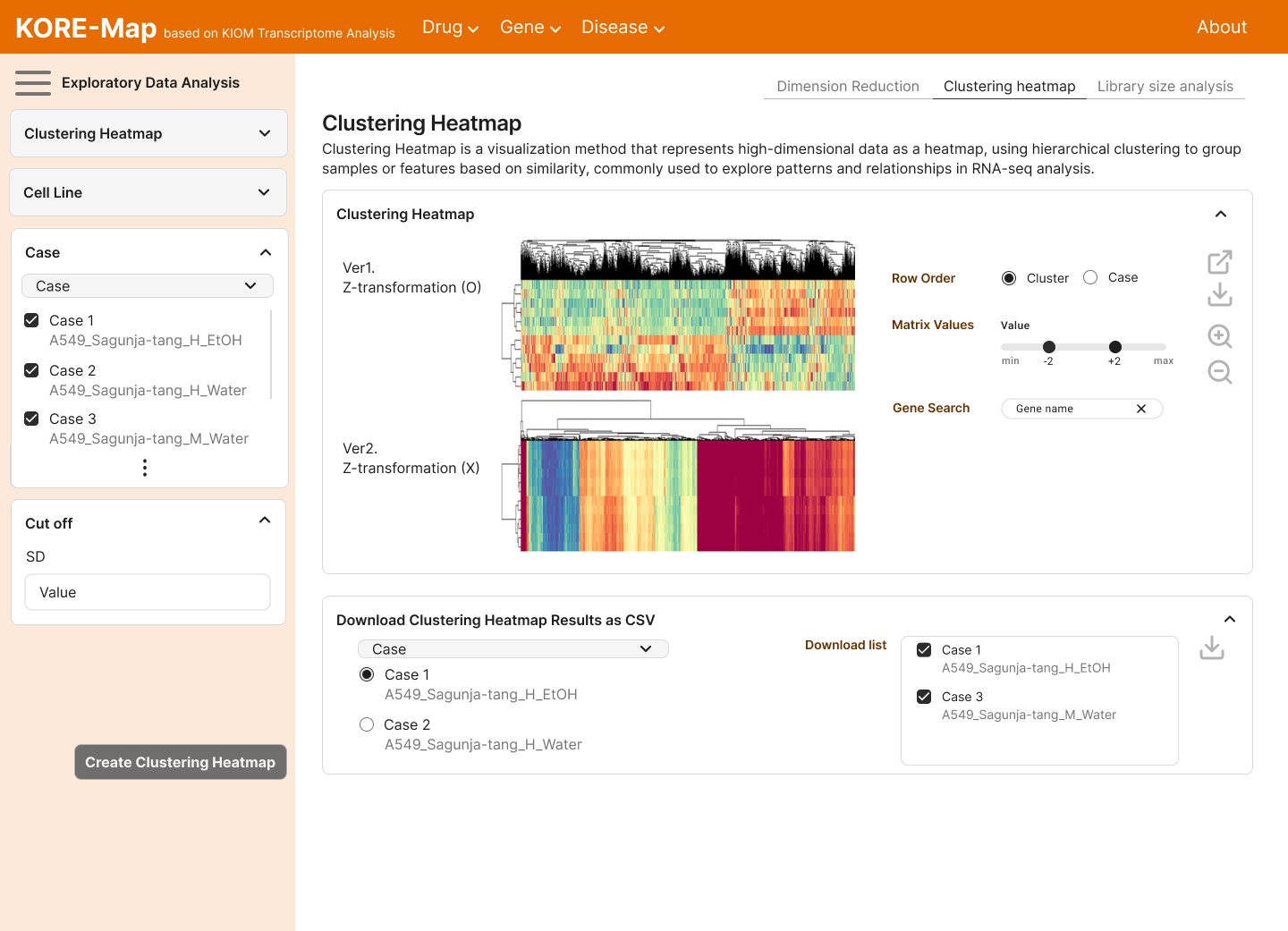
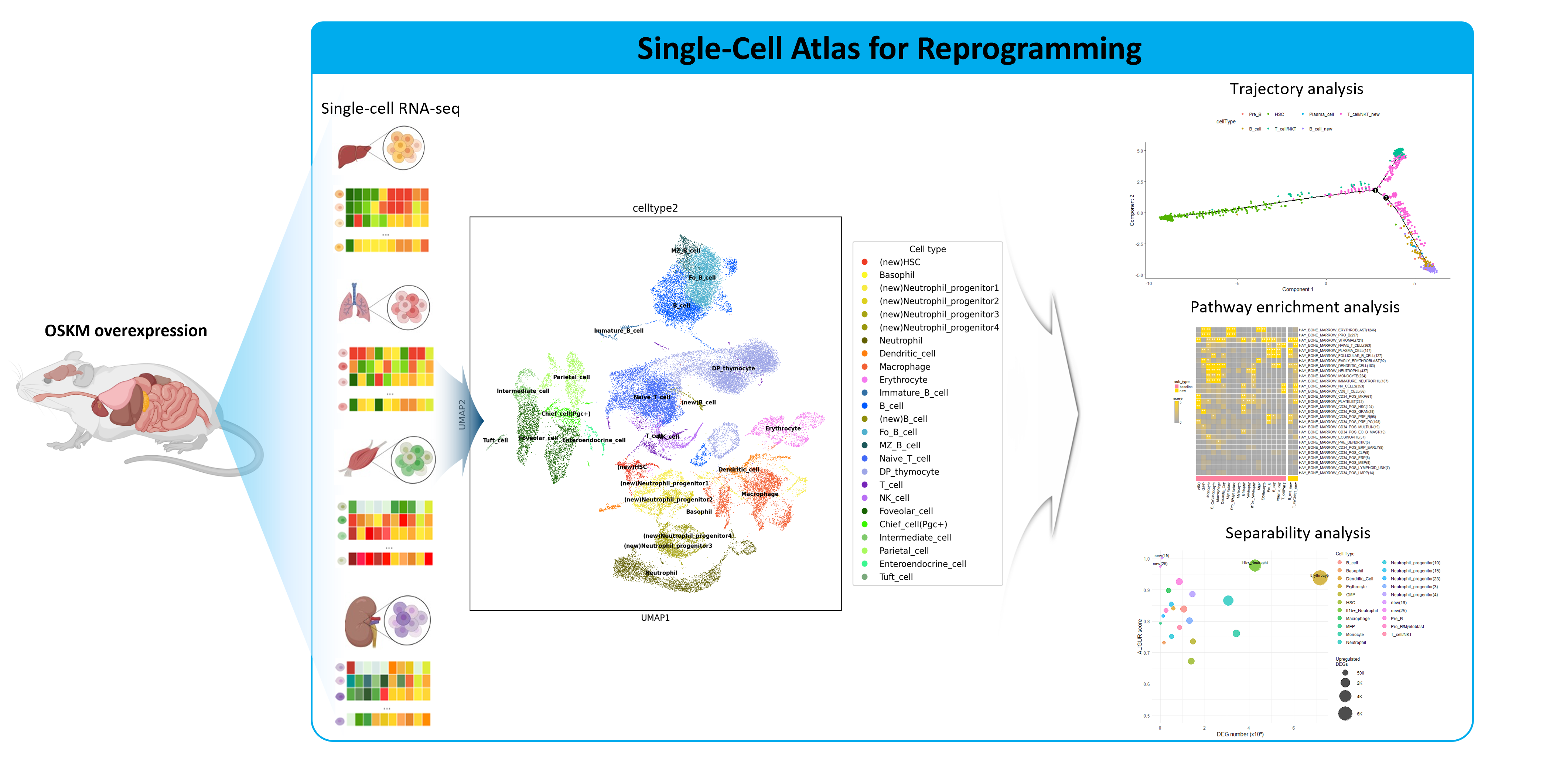
We create new value from data reuse. By harnessing large-scale public omics datasets generated under diverse disease models and experimental conditions, we redefine disease landscapes and uncover molecular targets for therapy. We also develop bioinformatics tools to interpret drug mechanisms from omics profiles perturbed by treatment.
What we value- Motivation : driving force to solve complex scientific puzzles to completion
- Integrity : ability to work productively with diverse teams and disciplines
- Balance : sustaining research momentum through dynamic interactions
 Systems Biology Lab
Systems Biology Lab